Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Author affiliation: Universidad Iberoamericana, Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic (R. Paulino-Ramirez, H. Lora-Rodriguez); Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA (W.R. Matias); Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston (W.R. Matias); Ministry of Health, Santo Domingo (G. Benoît, M. Thormann, R. Skewes-Ramm); Ministry of Defense, Santo Domingo (J. Ureña)
Mpox is a zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), which belongs to clade I (formerly Congo Basin clade) or clade II (formerly West Africa clade) (1). First identified in humans in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, mpox has become a global public health concern (2). As of December 2024, a total of 124,753 cases and 272 deaths have been reported in 128 countries; 54% of cases occurred in the Americas (3). Mpox spreads through close physical contact and fomites (4). Although sexual contact played a key role in the 2022–2023 mpox outbreak, nonsexual transmission also occurs, especially in children (5). In Latin America and the Caribbean, MPXV has circulated with varying disease outbreak intensity (6).
In the Dominican Republic, the first confirmed mpox case was reported in July 2022. We reviewed clinical and epidemiologic characteristics of reported cases to elucidate the epidemic in the Dominican Republic and guide public health efforts.
We conducted a retrospective review of the Dominican Republic’s national mpox database, which contains epidemiologic data collected by the Ministry of Public Health. Mpox is a reportable disease in the Dominican Republic, requiring healthcare workers to complete forms for suspected and confirmed cases, which are then uploaded to the national database. We analyzed data representing the initial outbreak period during July 2022–February 2023 and defined cases as suspected, probable, or confirmed by using World Health Organization criteria (7). Medical authorities interviewed patients suspected of having mpox and collected sociodemographic and clinical information; samples for MPXV testing were taken from lesions, exudates, crusts, and blood (if no rash was present). The National Public Health Laboratory conducted sample testing by MPXV PCR, targeting G2R and C3L loci according to World Health Organization guidelines (8); a positive PCR result confirmed diagnosis of mpox. After confirmation, Ministry of Public Health epidemiologists conducted mandatory reporting, contact tracing, and household contact testing. We categorized suspected cases as confirmed or negative. We used R version 4.3.2 (The R Project for Statistical Computing, https://www.r-project.org) for analyses.
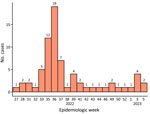
After the first mpox case was identified (July 2022), cases peaked in September and declined thereafter (Figure). Among 283 suspected cases, 71 (25.1%) were confirmed. Among confirmed mpox patients, 48 (67.6%) were male and 23 (32.4%) female; most (49.3%) male patients were 20–39 years of age. Sixteen (22.5%) confirmed mpox patients were children <10 years of age. Most (95.8%) confirmed mpox patients were born in the Dominican Republic; most (n = 39) cases occurred in the O Metropolitana region, encompassing Santo Domingo (Appendix Figure). We compiled sociodemographic and clinical characteristics (Table; Appendix Table). Most (90.1%) confirmed mpox patients manifested a rash, and 73.2% reported fever (>37.9°C; self-reported with or without a thermometer or measured by the person conducting household visits).
The Dominican Republic’s mpox outbreak revealed unique epidemiologic patterns compared with other outbreaks; a higher percentage of women (32.4%) and children <10 years of age (22.5%) was observed. The patterns resemble those in endemic countries in Africa but contrast with global trends during the 2022–2023 outbreak, where most cases occurred in adult men who have sex with men (MSM) and only 3.6% of women and 1.1% of children <17 years of age globally (9). This divergence reflects either genuine differences in transmission dynamics or underreporting among MSM because of stigma and homophobia, which are common in the Dominican Republic and heightened by the intersectionality of HIV (10). Societal stigma against MSM in the Dominican Republic might influence sexual networks, leading to concurrent relationships with both men and women, promoting mpox transmission into heterosexual households. Within households, mpox might spread via close contact, caregiving, and shared personal items, contributing to more cases among women and children. Those findings highlight the need for comprehensive public health approaches, including stigma reduction and fostering community trust. Further research is needed to clarify transmission and guide interventions.
Positive mpox cases were clinically similar to negative cases; most patients experienced a rash and fever. Although using rash and fever as screening criteria assists case identification, their lack of specificity poses challenges, particularly in settings with limited diagnostic capabilities. Combining clinical criteria with exposure history or risk profiles might improve testing efficiency in diagnostic-constrained settings. Expanding access to diagnostics and developing easy-to-use tests for resource-limited settings are critical for accurate case identification and optimized resource allocation.
The first limitation of our study is that data collected during outbreak investigations likely underestimate true incidence. Second, because of the evolving nature of the outbreak, comprehensive data, including sexual orientation, were not available.
In conclusion, we describe the initial mpox outbreak during July 2022–February 2023 in the Dominican Republic; the percentage of infected women and children was higher than expected compared with the global outbreak predominantly affecting MSM. Although the country successfully implemented mandatory reporting and vaccine deployment, challenges remain, such as incomplete data capture, limited access to PCR, and barriers to healthcare access. Addressing those gaps will be essential to improve outbreak detection and prepare for future mpox outbreaks.
Dr. Paulino-Ramirez is a principal investigator at Instituto de Medicina Tropical and Salud Global at Universidad Iberoamericana (UNIBE) in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic. His research and clinical interests focus on infectious diseases, HIV, emerging viruses, public health, and the implementation of preventive strategies, such as preexposure prophylaxis.